Data types in C language
The type of data that can be kept in a variable in a programming language is called data type. There are many types of data types such as integer, character, string, real etc. which are kept in a variable in any programming language. All these types are known as data types.
When we declare a variable during programming in the normal sense, then you have to tell the compiler what type of data you want to store in the variable, the compiler provides that much memory from the computer memory. With the ability to divide data into different types of language, you can easily work with complex programs. To know the difference between different types of data There are two reasons which are as follows -
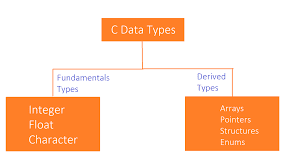
C Language supports the following data types.
There is any programming language like - c, c ++, java, php etc. There are data types which are important for programming. Whenever we create a program, we need some memory to run that program on the computer. And we can get this memory only with the help of data type, data type itself tells which type of value it is.
int 2 -32768 to 32767
short int 1 -128 to 127
long int 4 -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
signed int (for negative values) 2 -32768 to 32767
unsigned int 2 0 to 65535
Example: long int population = 200000000;
float 4 3.4E-38 to 3.4E + 38
double 8 1.7E-308 to 1.7E + 308
Example: double balance = 810.12354984;
Character data Type is used to store a character. They are divided into 2 categories.
Data type Size (Bytes) Range
char 1 -128 to 127
unsigned char 1 0 to 255
Example: char knowledge = "C";
Void data type is used in situations when you have no idea about the value. It is mostly used with functions. You can use Void type in C in these situations.
If your function does not return any value, you define its return type Void. For example, you can define a function like this. void myFunction ();.
If you are not taking any parameters in the function, then you can define Void there. Void type shows that no argument is taken in this function. For example, you can pass Void as a parameter like this. int myFunction (void);.
If you are not sure which type of variable will point to the variable then you can declare its type Void. After this you can point to any variable with a Void pointer.
Derived data type is used with the help of primary data type hence it is called derived data type. We will learn about all the derived data types in different tutorials.
When we declare a variable during programming in the normal sense, then you have to tell the compiler what type of data you want to store in the variable, the compiler provides that much memory from the computer memory. With the ability to divide data into different types of language, you can easily work with complex programs. To know the difference between different types of data There are two reasons which are as follows -
- The compiler, which translates the program into object code (as 0 and 1), can use the appropriate internal representation for each data type.
- While designing a program, programmers can use the correct operator to operate on data of every type.
C Language supports the following data types.
 |
Data types in C language |
There is any programming language like - c, c ++, java, php etc. There are data types which are important for programming. Whenever we create a program, we need some memory to run that program on the computer. And we can get this memory only with the help of data type, data type itself tells which type of value it is.
Fundamental Data type -: Primary data type is also called Fundamental data type. They are of the following types.
- int
- char
- float
- string
- All the "C" compiler supports five major primary data types named int, char, float, double and string.
Integre data type
Integer types are used to store any whole number (a number without a decimal). There are 5 types of Integer types. However, they all store complete numbers. But they are divided on the basis of memory size and range.
Data type Size (Bytes) Rangeint 2 -32768 to 32767
short int 1 -128 to 127
long int 4 -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
signed int (for negative values) 2 -32768 to 32767
unsigned int 2 0 to 65535
Example: long int population = 200000000;
Floating point data type
Floating point data type is defined to store numbers with decimals. Floating point data types are of 2 types. They are divided on the basis of size and range. In float type you can store up to 7 digits after decimal. Whereas up to 17 digits after the decimal can be stored in double type.
Data type Size (Bytes) Rangefloat 4 3.4E-38 to 3.4E + 38
double 8 1.7E-308 to 1.7E + 308
Example: double balance = 810.12354984;
Character data Type
Character data Type is used to store a character. They are divided into 2 categories.
Data type Size (Bytes) Range
char 1 -128 to 127
unsigned char 1 0 to 255
Example: char knowledge = "C";
Void data type
Void data type is used in situations when you have no idea about the value. It is mostly used with functions. You can use Void type in C in these situations.
If your function does not return any value, you define its return type Void. For example, you can define a function like this. void myFunction ();.
If you are not taking any parameters in the function, then you can define Void there. Void type shows that no argument is taken in this function. For example, you can pass Void as a parameter like this. int myFunction (void);.
If you are not sure which type of variable will point to the variable then you can declare its type Void. After this you can point to any variable with a Void pointer.
Derived data type in C
Derived data type is used with the help of primary data type hence it is called derived data type. We will learn about all the derived data types in different tutorials.
- Array type
- Pointer type
- Structure type
- Union type



Comments
Post a Comment
please leave your priceless comments thank you.